2021.03.18
Powerful stratospheric winds measured on Jupiter for the first time

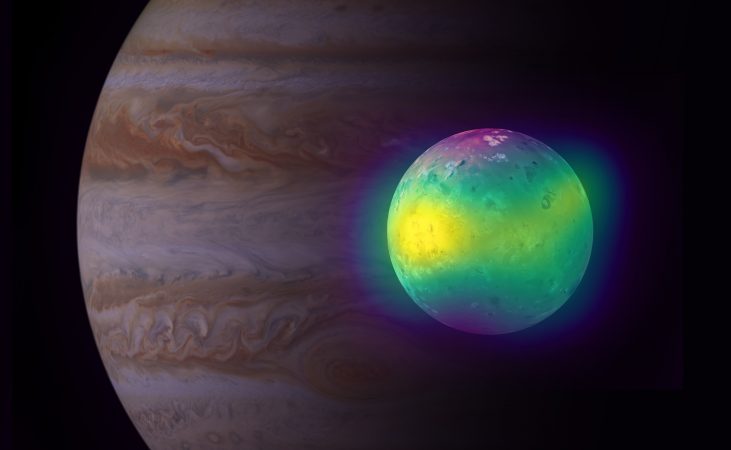
This image shows an artist’s impression of winds in Jupiter’s stratosphere near the planet’s south pole, with the blue lines representing wind speeds. These lines are superimposed on a real image of Jupiter, taken by the JunoCam imager aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft.
Credit: ESO/L. Calçada & NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS
Jupiter is famous for its distinctive red and white bands: swirling clouds of moving gas that astronomers traditionally use to track winds in Jupiter’s lower atmosphere. Astronomers have also seen, near Jupiter’s poles, the vivid glows known as aurorae, which appear to be associated with strong winds in the planet’s upper atmosphere. But until now, researchers had never been able to directly measure wind patterns in between these two atmospheric layers, in the stratosphere.
Measuring wind speeds in Jupiter’s stratosphere using cloud-tracking techniques is impossible because of the absence of clouds in this part of the atmosphere. However, astronomers were provided with an alternative measuring aid in the form of comet Shoemaker–Levy 9, which collided with the gas giant in spectacular fashion in 1994. This impact produced new molecules in Jupiter’s stratosphere, where they have been moving with the winds ever since.
A team of astronomers, led by Thibault Cavalié of the Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Bordeaux in France, have now tracked one of these molecules — hydrogen cyanide — to directly measure stratospheric “jets” on Jupiter. Scientists use the word “jets” to refer to narrow bands of wind in the atmosphere, like Earth’s jet streams.
“The most spectacular result is the presence of strong jets, with speeds of up to 400 meters per second, which are located under the aurorae near the poles,” says Cavalié. These wind speeds, equivalent to about 1450 kilometers an hour, are more than twice the maximum storm speeds reached in Jupiter’s Great Red Spot and over three times the wind speed measured on Earth’s strongest tornadoes.
“Our detection indicates that these jets could behave like a giant vortex with a diameter of up to four times that of Earth, and some 900 kilometers in height,” explains co-author Bilal Benmahi, also of the Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Bordeaux. “A vortex of this size would be a unique meteorological beast in our Solar System,” Cavalié adds.
Astronomers were aware of strong winds near Jupiter’s poles, but much higher up in the atmosphere, hundreds of kilometers above the focus area of the new study, which is published today in Astronomy & Astrophysics. Previous studies predicted that these upper-atmosphere winds would decrease in velocity and disappear well before reaching as deep as the stratosphere. “The new ALMA data tell us the contrary,” says Cavalié, adding that finding these strong stratospheric winds near Jupiter’s poles was a “real surprise”.
The team used 42 of ALMA’s 66 high-precision antennas, located in the Atacama Desert in northern Chile, to analyze the hydrogen cyanide molecules that have been moving around in Jupiter’s stratosphere since the impact of Shoemaker–Levy 9. The ALMA data allowed them to measure the Doppler shift — tiny changes in the frequency of the radiation emitted by the molecules — caused by the winds in this region of the planet. “By measuring this shift, we were able to deduce the speed of the winds much like one could deduce the speed of a passing train by the change in the frequency of the train whistle,” explains study co-author Vincent Hue, a planetary scientist at the Southwest Research Institute in the US.
In addition to the surprising polar winds, the team also used ALMA to confirm the existence of strong stratospheric winds around the planet’s equator, by directly measuring their speed, also for the first time. The jets spotted in this part of the planet have average speeds of about 600 kilometers an hour.
The ALMA observations required to track stratospheric winds in both the poles and equator of Jupiter took less than 30 minutes of telescope time. “The high levels of detail we achieved in this short time really demonstrate the power of the ALMA observations,” says Thomas Greathouse, a scientist at the Southwest Research Institute in the US and co-author of the study. “It is astounding to me to see the first direct measurement of these winds.”
“These ALMA results open a new window for the study of Jupiter’s auroral regions, which was really unexpected just a few months back,” says Cavalié. “They also set the stage for similar yet more extensive measurements to be made by the JUICE mission and its Submillimeter Wave Instrument,” Greathouse adds, referring to the European Space Agency’s JUpiter ICy moons Explorer, which is expected to launch into space next year.
This article is based on the press release issued by the European Southern Observtory on March 18 2021.
Paper information
These observation results were presented in Thibault Cavalié et al. “First direct measurement of auroral and equatorial jets in the stratosphere of Jupiter” in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics on March 18, 2021.
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of the European Southern Observatory (ESO), the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. ALMA is funded by ESO on behalf of its Member States, by NSF in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) in Taiwan and by NINS in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan and the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI).
ALMA construction and operations are led by ESO on behalf of its Member States; by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI), on behalf of North America; and by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) on behalf of East Asia. The Joint ALMA Observatory (JAO) provides the unified leadership and management of the construction, commissioning and operation of ALMA.